|
www.samuelprof.com |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
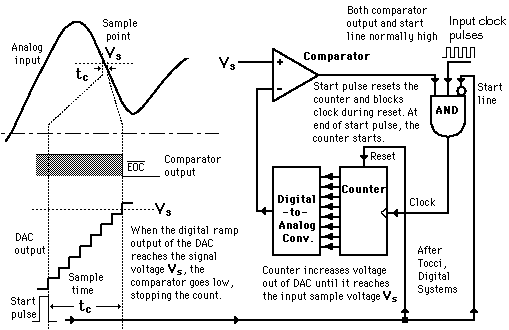
This is a sample of the large number of analog-to-digital conversion
methods. The basic principle of operation is to use the comparator principle to determine whether or not to turn on a particular bit of
the binary number output. It is typical for an ADC to use a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to determine one of the inputs to the comparator. Conversion from analog to digital form inherently involves comparator action where the value of the analog voltage at some point in time
is compared with some standard. A common way to do that is to apply the analog voltage to one terminal of a comparator and
trigger a binary counter which drives a DAC. The output of the DAC is applied to the other terminal of the comparator.
Since the output of the DAC is increasing with the counter, it will trigger the comparator at some point when its voltage
exceeds the analog input. The transition of the comparator stops the binary counter, which at that point holds the digital
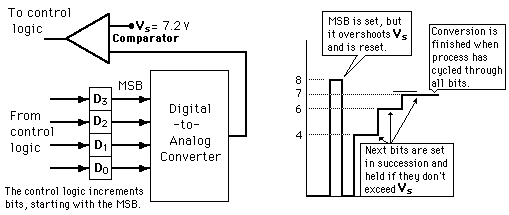
value corresponding to the analog voltage. Illustration of 4-bit SAC with 1 volt step size (after Tocci, Digital Systems). The successive approximation ADC is much faster than the digital
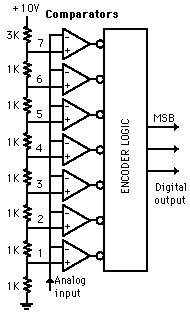
ramp ADC because it uses digital logic to converge on the value closest to the input voltage. A comparator and a DAC are used in the process. Illustrated is a 3-bit flash ADC with resolution 1 volt (after Tocci).
The resistor net and comparators provide an input to the combinational logic circuit, so the conversion
time is just the propagation delay through the network - it is not limited by the clock rate or some convergence sequence.
It is the fastest type of ADC available, but requires a comparator for each value of output (63 for 6-bit, 255 for 8-bit,
etc.) Such ADCs are available in IC form up to 8-bit and 10-bit flash ADCs (1023 comparators) are planned. The encoder logic
executes a truth table to convert the ladder of inputs to the binary number output. |